In a recent blog entry, Matt Cutts discusses a common response of sites that have been delisted or had their SERP position drop. Webmasters say that there’s nothing wrong with their site, that they haven’t been engaged in any shady link-building strategies, and Google is unfairly punishing them. Cutts responds that in many of these cases the reason for the penalty is that sites have been hacked and infected with malicious software without webmaster being aware.
Hacking a site is one of a number of Negative SEO strategies that a site’s competitors can engage in to damage search rankings and reputations. Today we’ll be having a look at hacking and a couple of other Negative SEO tactics, so that you can be aware of possible vectors of attack for your sites, and what you can do about them.
Hacked?
Hacking, or site intrusion, occurs when a malicious individual, usually exploiting some security vulnerability in a site’s software stack, gains access to a server and plants malware on it. The malware can then go on to affect the site’s visitors. When Google spots malware during a crawl, it will often delist a site to prevent its users becoming affected.
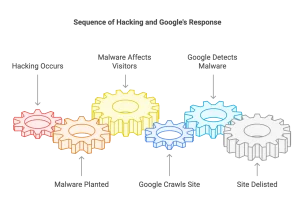
It’s more or less impossible to guarantee the security of an Internet-facing website, but it is possible to mitigate the risks of intrusion. It’s a webmaster’s responsibility to ensure that a site’s software is patched and upgraded, with all security releases applied in a timely fashion. There are various intrusion detection systems available, like Snort and Tripwire, that can monitor a site’s files, logs, and network traffic to determine when an intrusion occurs. If you determine that your site has been infected, have it professionally assessed and cleared, then request a malware review with Google Webmaster Tools.
Duplicate Content
Another favored tactic of those in the business of targeting competitor’s sites, is to take advantage of Google’s penalty for content duplication. Original material can be scraped from a site and then duplicated across numerous other locations on the web. To Google it appears that the target site is just one of the many sites with the same content, and ranking will take a hit accordingly. This one is actually a little more difficult to deal with than a site intrusion, because the servers involved are not directly accessible by the owners of the target site. Often, affected site owners will have to resort to legal remedies, including using the DMCA to get material that infringes copyright taken down.
Link Spamming
As you will know from our previous article, maintaining a natural and balanced backlink profile is an important part of SEO. It is possible for competitors to interfere with link-building efforts by link-spamming with links to your site on low-quality, unrelated sites, thus skewing a backlink profile. If a site has taken a hit in its rankings, the owners should do a thorough appraisal of their backlink profile using tools like Open Site Explorer.
It’s theoretically possible for many of Google’s signals to be used to target a competitor’s sites. Let us know in the comments if you’ve had experience of negative SEO, and what you did about it.